STL Algorithm: Land of Permutation
- 13 分钟前Heap Oeration
- make_heap:建堆;
- is_heap:判断是否为堆;
- pop_heap:获取堆顶元素;
- push_heap: 向堆中添加元素,并重新建堆;
- sort_heap: 对堆进行排序。
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
#include <string_view>
using namespace std;
//C++17中我们可以使用std::string_view来获取一个字符串的视图,
//字符串视图并不真正的创建或者拷贝字符串,而只是拥有一个字符串的查看功能。
void print(string_view text, vector<int> const& v = {}){
cout << text << ": ";
for(const auto & e : v){
cout << e << ' ';
}
cout << endl;
}
void print(vector<int> const & v){
if(is_heap(v.begin(), v.end()))
cout << "v is a Max heap. \n";
else if(is_heap(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<>{})){
cout << "v is a Min heap. \n";
} else{
cout << "v is not a heap. \n" ;
}
}
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
cout << "Max Heap: " << endl;
vector<int> v { 3, 2, 4 ,1 , 5, 9};
print("initially, v" , v);
print(v);
make_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print("make heap, v", v);
print(v);
// move largest element to back;
pop_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print("pop_heap, v", v);
auto top = v.back();
v.pop_back();
print("former top element", {top});
print("after removing the former top element, v", v);
v.push_back(99);
push_heap (v.begin(),v.end());
print("after push 99 to heap, v" , v);
sort_heap(v.begin(), v.end());
print("after sort heap, v", v);
cout << "\nMin Heap: " << endl;
vector<int> v1 { 3, 2, 4, 1, 5, 9};
print("initially, v1", v1);
print(v1);
make_heap(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<>{});
print("after make_heap,v1" , v1 );
print(v1);
pop_heap(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<>{});
print("after pop_heap, v1", v1);
auto top1 = v1.back();
v1.pop_back();
print("fromer top element: ", {top1});
print("after removing the former top element, v1", v1);
v1.push_back(99);
push_heap (v1.begin(),v1.end(), greater<>{});
print("after push 99 to heap, v1" , v1);
sort_heap(v1.begin(), v1.end(), greater<>{});
print("after sort heap, v1", v1);
return 0;
}
Max Heap:
initially, v: 3 2 4 1 5 9
v is not a heap.
make heap, v: 9 5 4 1 2 3
v is a Max heap.
pop_heap, v: 5 3 4 1 2 9
former top element: 9
after removing the former top element, v: 5 3 4 1 2
after push 99 to heap, v: 99 3 5 1 2 4
after sort heap, v: 1 2 3 4 5 99
Min Heap:
initially, v1: 3 2 4 1 5 9
v is not a heap.
after make_heap,v1: 1 2 4 3 5 9
v is a Min heap.
after pop_heap, v1: 2 3 4 9 5 1
fromer top element: : 1
after removing the former top element, v1: 2 3 4 9 5
after push 99 to heap, v1: 2 3 4 9 5 99
after sort heap, v1: 99 9 5 4 3 2
SORTING
sort 函数的四种用法:
- 默认升序;
- 默认降序排列;
- 自定义类型的排序;
- lambda 表达式;
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <array>
#include <string_view>
using namespace std;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
array<int, 10> arr = {5, 7, 4, 2, 8, 6, 1, 9, 0, 3};
// lambda expression print
auto print = [&arr](string_view const str){
for(auto a : arr){
cout << a << ' ';
}
cout << ": " << str << endl;
};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
print("sorted with the default operator< ");
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), greater<>());
print("sorted with the standard library compare function object");
struct {
bool operator()(int a, int b) const {return a< b;}
}customLess;
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), customLess);
print("sorted with a custom function object");
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end(), [](int a, int b){
return a > b;
});
print("sorted with a lambda expression");
return 0;
}
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : sorted with the default operator<
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 : sorted with the standard library compare function object
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 : sorted with a custom function object
9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 : sorted with a lambda expression
partial_sort 用法:
- 默认升序排列前 n 项
- 使用 lambda 表达式作为排序方式
array<int, 10> arr = {5, 7, 4, 2, 8, 6, 1, 9, 0, 3};
partial_sort(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + 3, arr.end());
print("partial sorted with the deafult comparison (operator<");
partial_sort(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + 5, arr.end(), [](int a, int b) {
return a > b;
});
print("partial sorted with the lambda expression >");
0 1 2 7 8 6 5 9 4 3 : partial sorted with the deafult comparison (operator<
9 8 7 6 5 0 1 2 4 3 : partial sorted with the lambda expression >
nth_elements: 排序后前 n -1 个都小于第 n 个元素,后面的都大于等于第n个元素;
array<int, 10> arr = {5, 7, 4, 2, 8, 6, 1, 9, 0, 3};
nth_element(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + 5, arr.end());
print("after nth_element with the default comparison");
cout << "the 5th big element in array is " << arr[5] << endl;
nth_element(arr.begin(), arr.begin()+5, arr.end(), greater<int>());
print("after nth_element with the greater comparison");
cout << "the 5th little element in array is " << arr[5] << endl;
3 0 4 2 1 5 8 9 7 6 : after nth_element with the default comparison
the 5th big element in array is 5
6 7 9 8 5 4 3 2 1 0 : after nth_element with the greater comparison
the 5th little element in array is 4
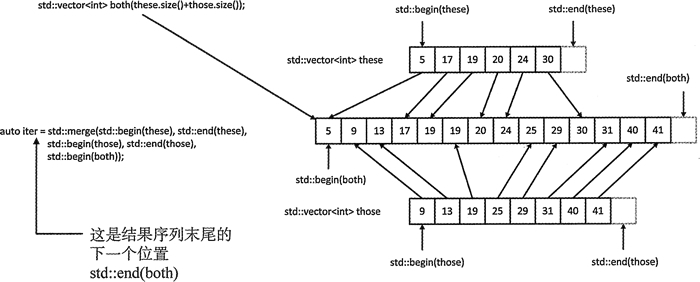
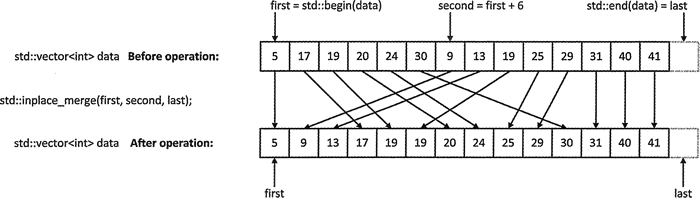
merge 和 inplace_merge1: merge 是将两个序列合并成一个有序序列, inplace_merge 是将同一个序列中,两个连续有序的元素序列合并为一整个有序的序列。
array<int, 10> arr = {5, 7, 4, 2, 8, 6, 1, 9, 0, 3};
auto print = [&](vector<int> &arr, string_view const str){
for(auto a : arr){
cout << a << ' ';
}
cout << ": " << str << endl;
};
array<int, 5> arr2 = {2, 3, 4, 5, 6};
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
vector<int> result(arr.size() + arr2.size());
merge(arr.begin(), arr.end(), arr2.begin(), arr2.end(), result.begin());
print(result, "after merged two increase array");
//将 arr 和 arr1 copy 到 result 序列中,此时 result 中 arr 有序,arr2 也是有序
auto it = copy(arr.begin(),arr.end(), result.begin());
copy(arr2.begin(), arr2.end(), it);
inplace_merge(result.begin(), result.begin() + arr.size(), result.end());
print(result, "after inplaced merged two increase array");
0 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 9 : after merged two increase array
0 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7 8 9 : after inplaced merged two increase arr
Partitioning
partition: 以某种方式将序列分为两部分,下面展示一个按是否为奇数分的方式,调用 partition 方法后,序列前半部分均为奇数,后半部分均为偶数;
partition_point: 指示其分区点。
print("initially array.");
partition(arr.begin(), arr.end(), [](int i)-> bool { return i & 1;});
print("after partition if odd.");
auto it = partition_point(arr.begin(), arr.end(), [](int i) -> bool { return i & 1;});
cout << "partition point is " << *it << endl;
5 7 4 2 8 6 1 9 0 3 : initially array.
5 7 3 9 1 6 8 2 0 4 : after partition if odd.
partition point is 6
Other Permutation
print("initially array.");
rotate(arr.begin(), arr.begin() + 3, arr.end());
print("after rotate 3 times.");
unsigned seed = std::chrono::system_clock::now().time_since_epoch().count();
shuffle(arr.begin(), arr.end(), default_random_engine(seed));
print("after shuffleed.");
reverse(arr.begin(), arr.end());
print("after reversed.");
5 7 4 2 8 6 1 9 0 3 : initially array.
2 8 6 1 9 0 3 5 7 4 : after rotate 3 times.
7 3 2 5 9 0 1 8 6 4 : after shuffleed.
4 6 8 1 0 9 5 2 3 7 : after reversed.
还有两个用于排列组合的 STL 算法:
- next_permutation
- pre_permutation

