C++ 17 新特性
- 19 分钟前基本语言特性
1. 结构化绑定(Structured Bindings)
将一个对象绑定到 匿名对象,结构化绑定时引入的新变量名实际上都指向这个匿名对象的成员/元素。
struct MyStruct {
int i = 0;
std::string s;
};
MyStruct ms{40, "uncle"};
auto [u, v] = ms; // u = 40, v = "uncle"
auto [u2, v2] {ms}; // 同上
auto [u3, v3] (ms); // 同上
u = 55;
ms.i = 90;
std::cout << u << " " << ms.i << std::endl; // 55 90
const auto& [u4, v4] = ms;
ms.i = 100;
std::cout << u4 << " " << ms.i << std::endl; // 100 100
auto&& [u6, v6] = std::move(ms);
std::cout << "ms.s: " << ms.s << std::endl; // uncle
std::string s = std::move(v6);
std::cout << "ms.s: " << ms.s << std::endl; // ms.s:
std::cout << "v6: " << v6 << std::endl; // v6:
std::cout << "s: " << s << std::endl; // uncle
结构化绑定适用于任何有public数据成员的结构体、 C风格数组和“类似元组(tuple-like)的对象。
- 对于所有非静态数据成员都是
public的 结构体和类 , 你可以把每一个成员绑定到一个新的变量名上。 - 对于 原生数组 ,你可以把数组的每一个元素都绑定到新的变量名上。
- 对于任何类型,你可以使用 tuple-like API 来绑定新的名称, 无论这套API是如何定义“元素”的。对于一个类型 type 这套API需要如下的组件:
std::tuple_size<type>::value要返回元素的数量。std::tuple_element<idx, type>::type要返回第idx个元素的类型。- 一个全局或成员函数
get<idx>()要返回第idx个元素的值。
// until c++ 17
for (const auto& elem : mymap) {
std::cout << elem.first << ": " << elem.second << '\n';
}
// since c++ 17
for (const auto& [key, val] : mymap) {
std::cout << key << ": " << val << '\n';
}
2. 带初始化的 if 和 switch 语句
if 和 switch 语句允许在条件表达式中添加一条初始化语句:
// s 初始化后在 if 语句中有效,包括 else 分支里。
if(status s = check(); s != status::success) {
return s;
}
// example: 声明一个文件系统路径,根据类别进行处理
namespace fs = std::filesystem;
switch (fs::path p{name}; status(p).type()) {
case fs::file_type::not_found:
std::cout << p << " not found\n";
break;
case fs::file_type::directory:
std::cout << p << ":\n";
for (const auto& e : std::filesystem::directory_iterator{p}) {
std::cout << "- " << e.path() << '\n';
}
break;
default:
std::cout << p << " exists\n";
break;
}
3. 内联变量
c++17 之前不允许在类内初始化非常量静态成员,而且在类外初始化非常量静态成员如果被多个 cpp 文件同时包含会引起新的链接 Error.
// before c++ 17
class MyClass {
static std::string msg{"OK"}; // 编译期ERROR ...
};
class MyClass {
static std::string msg;
};
std::string MyClass::msg{"OK"}; // 如果被多个CPP文件包含会导致链接ERROR
// since c++ 17
class A {
public:
inline static int a = 100; // ok
};
inline A a; // 多个 cpp 文件包含也 ok,只要一个编译单元内没有重复的定义即可。
inline 变量保证 即使定义所在的头文件被多个 CPP 文件包含,也只会有一个全局对象。
constexpr static 隐含 inline:
struct D {
static constexpr int n = 5;
};
// constexpr int D::n; // c++ 14 必须添加该条声明语句,c++17 弃用
const int* p = &D::n; // c++14: Undefined symbols for architecture x86_64: "D::n", c++17 ok
4. 聚合体扩展(Aggregate with base classes)
聚合体:数组或者 C 风格的简单类,简单类要求没有用户定义的构造函数、没有私有或保护的非静态数据成员、没有虚函数,在 C++17 之前,还要求没有继承。
struct Data {
int i;
double d;
};
struct MoreData : Data {
bool flag;
//MoreData (int i, double d, bool b) : Data{i, d}, flag{b} {} // c++14 需要额外添加 ctor
};
int main() {
Data x{1, 0.1};
MoreData y{2, 0.2, true}; // c++17 ok, c++ 14 error: no matching constructor for initialization of 'MoreData'
MoreData z1{}; // all members initialize with value 0
MoreData z2; // all members are undefined
MoreData z3{{3}}; // {{3, 0}, false}
MoreData z4{{}, true}; // {{0, 0}, true}
}
- 可以跳过一些值去初始化,被跳过的成员会进行默认初始化(基础类型初始化为 0、false 或 nullptr,类会默认构造);
- 使用花括号和不使用花括号完全不同:
- z1 的成员默认初始化为 0;
- z2 的定义没有初始化任何成员,所有成员的值都是未定义的;
- 内部嵌套的初值列表将按照继承时基类声明的顺序传递给基类;
template<typename T>
struct D : std::string, std::complex<T>
{
std::string data;
};
int main() {
D<float> s{{"hello"}, {4.5, 4.6}, "world"};
D<float> t{"hello", {4.5, 6.7}, "world"};
std::cout << static_cast<std::string>(s) << s.data << std::endl;
std::cout << static_cast<std::complex<float>>(t) << std::endl;
}
- c++ 17 引入 is_aggregate<> 测试一个类型是否为聚合体;
std::cout << std::is_aggregate<decltype(s)>::value; // 输出1(true)
std::cout << std::is_aggregate<decltype(s.data)>::value; // 输出0(false)
5. 强制省略拷贝或传递未实例化的对象(Mandatory Copy Elision or Passing Unmaterialized Objects)
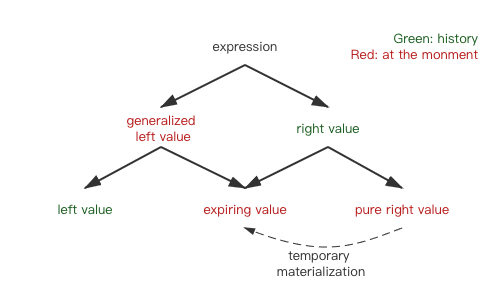
C++ 值类型体系: 视频: Back to Basics: understanding value categories
- An lvalue is an expression referring to an object, and an objedct is a region of storage.
- An rvalue is simply an expression that’s not an lvalue.
Conceptually, rvalue of class type do occupy data storage. And conceptually, rvalues of build-in types don’t occupy data storage. However, the tempory object created is still an rvalue, but it occupies data storage. So there are two kinds of rvalues.
- prvalue: pure right valu, which do not occupy data storage.
- xvalue: expiring, which do occupy data storage.
- The temporary object is created through a temporary materialization conversion. It converts a prvalue to into an xvalue.
string s = "hello"; string t = "world"; s = s + ", " + t; // compiler: s = s + string(", ") + t, lvalue + rvalue + lvalue
C++14 使用临时对象来初始化要求类中必须有隐式或显式的 copy or move ctor. C++ 17 用临时变量(prvalue)初始化对象时 copy elision 是强制性的。
class A {
public:
A(const A&) = delete;
A(A&&) = delete;
};
void foo(A param) {}
A bar() {
return A{};
}
int main() {
foo(A{}); // 临时对象 A{} 初始化 param, c++14 error, c++17 ok
A x = bar(); // 返回的临时对象初始化 x, c++14 error, c++17 ok
foo(bar()); // 返回的临时对象初始化 param, c++14 error, c++17 ok
return 0;
}
强制 copy elision 的作用:
- 减少临时变量 copy 带来更好的性能;
- 可以定义一个总是可以工作的工厂函数;
- 对于移动构造函数被显式删除的类,也可以返回临时对象来初始化新的对象;
6. lambda 表达式扩展
6.1 constexpr lanmbda ,编译期 lambda
从 c++ 17 开始,lambda 表达式会尽可能的隐式声明未 constexpr.
任何只使用有效的编译期上下文 (例如,只有字面量,没有静态变量,没有虚函数,没有 try/catch,没有 new/delete 的上下文)的 lambda 都可以被用于编译期。
auto squared = [](auto val) { // 隐式声明为 constexpr,编译期 lambda
return val * val;
};
std::array<int, squared(5)> a; // c++ 14 error: non-type template argument is not a constant expression, c++17: std::array<int, 25>
auto squared2 = [](auto val) constexpr {
static int tmp = 0; //c++17 error: static variable not permitted in a constexpr function
return val * val;
};
一个隐式或显式的 constexpr lambda 的函数调用符也是 constexpr.
auto squared = [](auto val) {
return val * val;
};
// 上述代码会转换为如下闭包类型
class CompilerSpecificName {
public:
...
template<typename T>
constexpr auto operator() (T val) const {
return val*val;
}
};
以下两种不同定义:
auto squared1 = [](auto val) constexpr { // 编译期 lambda 调用,运行时初始化 squared1
return val * val;
};
constexpr auto squared2 = [](auto val) { // 编译期初始化 squared2
return val * val;
};
std::array<int, squared1(5)> a;
std::array<int, squared2(5)> b;
如果静态初始化顺序很重要那么可能导致问题,可能会导致 static initialization order fiasco。
没整明白
6.2 capturing *this
在非静态成员函数中,如果不捕获 this,不能在 lambda 函数内部访问任何类成员。
class C {
private:
std::string name;
public:
void foo() {
auto l1 = [] { std::cout << name << '\n'; }; // error: 'this' cannot be implicitly captured in this context
auto l2 = [] { std::cout << this->name << '\n'; }; // ERROR
}
};
c++ 11 和 14 以值或引用的方式捕获 this 指针。当对象的生命周期结束,而 lambda 的生命周期还没有结束时,就会出现问题。比如在 lambda 中 开启一个新的线程来完成某些任务。c++ 14 提供的以拷贝方式捕获 this 指针的解决方案是 [self = *this]{ self.f(); } ,c++ 17 的更新是:[*this]{ f(); },优化了写法。
7. 新属性(attributes)
[[nodiscard]]鼓励编译器在某个函数的返回值未被使用时给出警告;- 内存泄漏,例如返回值中含有动态分配的内存,但并未使用;
- 不必要的开销,例如由于返回值没使用而导致的一些奇怪的行为;
[[maybe_unused]]避免编译器在某个变量未被使用时发出警告;[[fallthrough]]可以避免编译器在 switch 语句中某一个标签缺少 break 语句时发出警告;
通用属性扩展
- 属性可以用于标记命名空间;
namespace [[deprecated]] Draft {}
- 属性可以用于标记枚举类型的值;
enum class City {
Berlin = 0,
NewYork = 1,
Mumbai = 2,
Bombay [[deprecated]] = Mumbai,
};
- 对于用户自定义的属性,可以使用 using 前缀避免为每一个属性重复输入命名空间;
// until c++17
[[MyLib::WebService, MyLib::RestService, MyLib::doc("html")]] void foo();
// since c++17
[[using MyLib: WebService, RestService, doc("html")]] void foo();
8. 嵌套命名空间
namespace A::B::C {
//...
}
namespace A {
namespace B {
namespace C {
//...
}
}
}
9. 更严格的表达式求值顺序 (Stricter order of expression evaluation)
- e1 保证在 e2 前求值:
- e1[e2]
- e1.e2
- e1.*e2
- e1 -> *e2
- e1 « e2
- e1 » e2
- 所有的赋值运算右侧值保证会在左侧值之前求值;
new Type(e)中保证内存分配的操作在对 e 求值之前发生。
10. 用整型初始化 enum 值
enum Month : char {};
Month May{5}; // c++14 error: cannot initialize a variable of type 'Month' with an rvalue of type 'int', 17ok
11. 修正 auto 类型的列表初始化
// cpp 11
int x{42}; // 初始化一个int
int y{1, 2, 3}; // ERROR
auto a{42}; // 初始化一个std::initializer_list<int>
auto b{1, 2, 3}; // OK:初始化一个std::initializer_list<int>,
// cpp 17
auto a{42}; // 初始化一个int
auto b{1, 2, 3}; // ERROR
当使用 auto 进行拷贝列表初始化(使用了 =)时仍然是初始化一个 std::initializer_list<>:
auto c = {42}; // 仍然初始化一个std::initializer_list<int>
auto d = {1, 2, 3}; // 仍然OK:初始化一个std::initializer_list<int>
12. Hexadecimal floating point literals
具有十六进制基数和十进制指数的浮点文字:0xC.68p 2, 0x1.P-126。 C 从 C99 开始就支持这种语法,printf(“%a”) 。
- 有效数字/尾数用十六进制书写;
- 指数部分用十进制书写,表示乘以2的n次幂
13. UTF-8 创建字符
auto c = u8'6'; // UTF-8编码的字符6
在 C++17 中,u8’6’ 的类型是 char,在 C++20 中可能会变为 char8_t。
- u8用于单字节USASCII和UTF8编码;
- u用于两字节的UTF16编码;
- U用于四字节的UTF32编码;
- L用于没有明确编码的宽字符,可能是两个或者四个字节;
14. made noexcept part of type system
以 noexcept 修饰的函数和没有noexcept修饰的函数是不同类型,会导致函数重载;
void nonthrowing_func() noexcept {} // or noexcept(true)
void throwing_func() noexcept(false) {}
void call_func_ptr(void (*fp)() noexcept) noexcept {
fp();
}
template <typename T>
void call_func_ptr2(T) {}
template <>
void call_func_ptr2(void (*fp)() noexcept) {}
int main() {
call_func_ptr(nonthrowing_func); // fp()
// call_func_ptr(throwing_func); // error, no known conversion from 'void () noexcept(false)' to 'void (*)() noexcept' for 1st argument
call_func_ptr2(nonthrowing_func); // call_func_ptr2 fp,
call_func_ptr2(throwing_func); // c++17 call_func_ptr2 T, c++14 error: target exception specification is not superset of source
return 0;
}
Before C++ 17 :
The noexcept-specification is not a part of the function type (just like dynamic exception specification) and can only appear as a part of a lambda declarator or a top-level function declarator when declaring functions, variables, non-static data members of type function, pointer to function, reference to function, or pointer to member function, and also when declaring a parameter or a return type in one of those declarations that in turn happens to be a pointer or reference to function. It cannot appear in a typedef or type alias declaration.
void f() noexcept; // the function f() does not throw void (*fp)() noexcept(false); // fp points to a function that may throw void g(void pfa() noexcept); // g takes a pointer to function that doesn't throw // typedef int (*pf)() noexcept; // error
15. 单参数 static_assert
#include <type_traits>
template<typename T>
class C {
static_assert(std::is_default_constructible<T>::value, "class C: elements must be default-constructible");
static_assert(std::is_default_constructible_v<T>); // cpp14 error, cpp17 ok
};
16. 预处理条件 __has_include
添加了一个检查某个头文件是否可以被包含的宏:
#if __has_include(<filesystem>)
# include <filesystem>
# define HAS_FILESYSTEM 1
#elif __has_include(<experimental/filesystem>)
# include <experimental/filesystem>
# define HAS_FILESYSTEM 1
# define FILESYSTEM_IS_EXPERIMENTAL 1
#elif __has_include("filesystem.hpp")
# include "filesystem.hpp"
# define HAS_FILESYSTEM 1
# define FILESYSTEM_IS_EXPERIMENTAL 1
#else
# define HAS_FILESYSTEM 0
#endif
模版相关
17. Class template argument deduction
// until cpp17
std::complex<double> c{5.1, 3.3};
std::mutex mx;
std::lock_guard<std::mutex> lg(mx);
// since cpp17
std::complex c{5.1, 3.3}; // OK:推导出std::complex<double>
std::mutex mx;
std::lock_guard lg{mx}; // OK:推导出std::lock_guard<std::mutex>
// containner
std::vector v1 {1, 2, 3}; // OK:推导出std::vector<int>
std::vector v2 {"hello", "world"}; // OK:推导出std::vector<const char*>
18. template <auto>
template <auto X>
struct constant {
static constexpr auto value = X;
};
enum TestEnum { VAL1, VAL2, };
int main() {
// cpp 14: error: 'auto' not allowed in template parameter until C++17
constant<5> b1; // OK: template parameter type is int
constant<'a'> b2; // OK: template parameter type is char
constant<VAL1> b3; // decltype(X) == TestEnum
return 0;
}
19. 折叠表达式(Fold expression)
template<typename... T>
auto foldSum(T... arg) {
return (... + arg);
}
int main() {
std::cout << foldSum(1, 2, 3, 4) << std::endl;
return 0;
}
20. constexpr if
template <typename T>
std::string asString(T x)
{
if constexpr(std::is_same_v<T, std::string>) {
return x; // 如果T不能自动转换为string该语句将无效
}
else if constexpr(std::is_arithmetic_v<T>) {
return std::to_string(x); // 如果T不是数字类型该语句将无效
}
else {
return std::string(x); // 如果不能转换为string该语句将无效
}
}
部分其他特性
- std::byte: 在
<cstddef>中定义了一个新的字节类型,代表内存的最小单位。 - std::any: 一种在保证类型安全的基础上还能改变自身类型的值类型;
- std::string_view: 一个 string_view 对象可以看作是 string 的引用;
- std::optional<> 模拟了一个可以为空的任意类型的实例。
- std::variant<>:A value of
variant<A, B, C>contains one of anA, aB, or aCat any one time.
移除或弃用的特性
Removed
- auto_ptr, random_shuffle,
<functional>中过时的部分: cpp11使用 unique_ptr 替代,cpp17 移除; ??!- register: 依然是关键字,但不具有任何语义;
- 不再支持 bool 类型的 ++ 操作:bool++, ++bool;
- iostream 中被弃用的一些别名;
- 动态异常声明 throw(A, B, C);
- function<> 的 allocator 支持;
Depracated
- 弃用静态 constexpr 类成员的重新声明;
- 弃用 c 库头文件,比如
<ccomplex>等等; - result_of
- shared_ptr::unique
- 暂时弃用
memory_order_consume;
References: